greenspecR&D
OCT
Optical Coherence Tomography
Sketch of working principle

- • TDOCT: MIT (J.G. Fujimoto et al.) in 1991.
- • FDOCT has been researching since 1995.
Advantages
- • Noninvasive in vivo imaging
- • High spatial resolution
- • Broad dynamic range
Disadvantages
- • Coherent noise
- • Dispersion mismatch
Applications
-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

-
Mouse Cornea

[M. Wojtkowski et al., Opt. Exp., v.10, 2004][Karin Wiesauer et al., Opt. Exp., v.13, 2005]
Measurement Image
-

Ophthalmology
(안과학) -

Gastroenterology
(위장병학) -

Urology
(비뇨기학) -

Gynecology
(부인과의학) -

Ophthalmology
(안과학) -

Gastroenterology
(위장병학) -

Urology
(비뇨기학) -

Gynecology
(부인과의학)
Optical Coherence Tomography
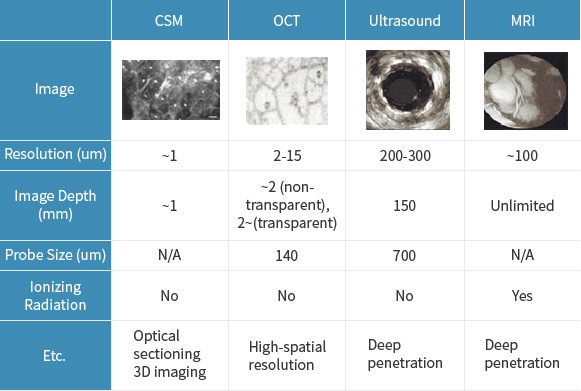
[E.Regar J.A. et al., Cardio. Radi. Med. v.4, 2003]
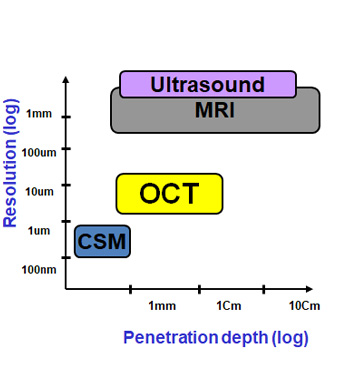
- • Resolution 10 times higher than Ultrasound, MRI
- • Penetration depth deeper than CSM
- • Enough niche market against other imaging technologies
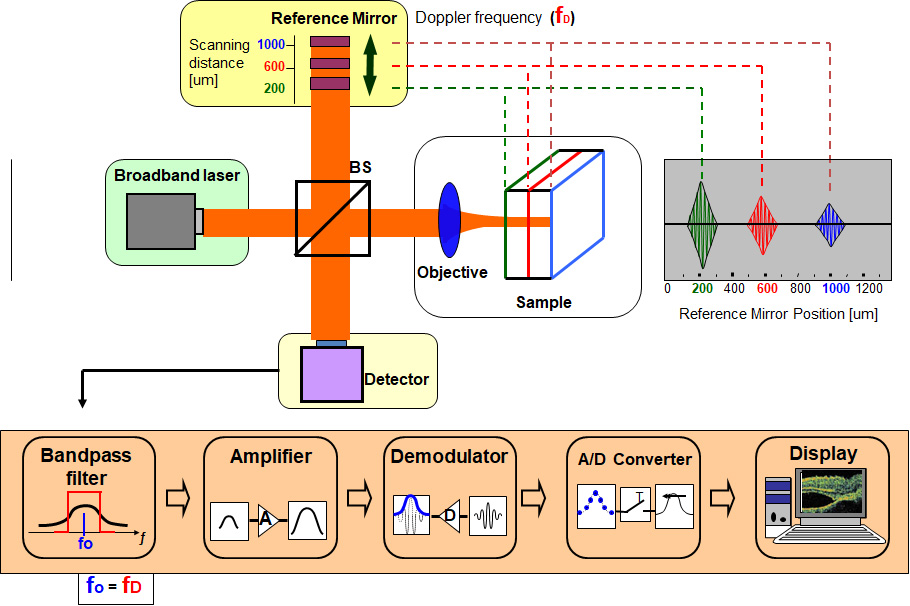
Principle of Time Domain OCT
Principle of Spectral Domain OCT
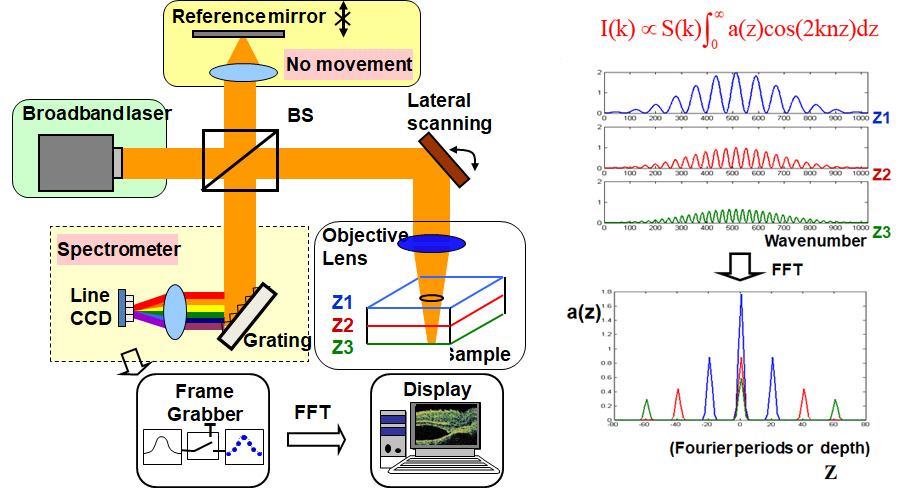
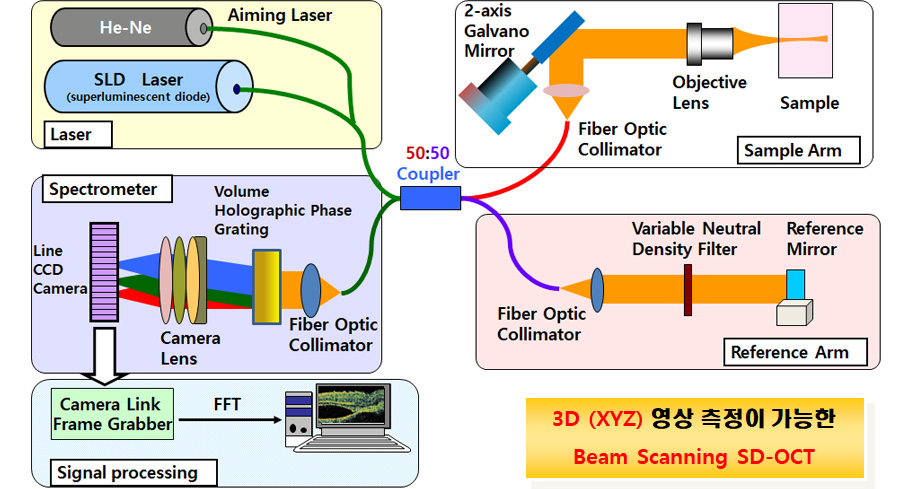
Schematic diagram of SD OCT
Measurement Image
-
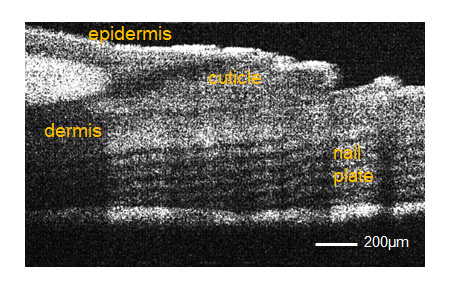
Human nail fold
-

Firefly light organ
-

Mouse brain
-

Human fingerprint
